Hello fellow UCWbLers, my name is Megan L., and post is going to contain some strategies I have developed for tutoring a literature review after doing a good chunk of research on the topic for my WRD 395 class (the one that prepares us to be tutors) with Erin.
I decided to focus my research on literature reviews after having a writer bring one in to review in an appointment. It was in this very moment that I realized that I, in fact, had no idea what a literature review was. Thus, the research was born!
First, I’m going to start off with a brief overview of what a literature review is (for those of you who are in a similar boat as me).
The Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill defines a literature review as something that “discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. A literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis,”.
While most students feel comfortable with the summary aspect of this style of writing, synthesizing is a bit more difficult. A study conducted by Jonathan Cisco over the course of three years in a university writing center confirmed this fact. Cisco found that the majority of the writers he encountered not only were unsure of how to structure a literature review, but lacked a basic understanding of what it was.
This research contributed to the creation of the Literature Review Lesson (LRL) which gave students a specific framework to build a theme-based literature review within. I have included some helpful graphics from Cisco’s piece below.

(This is what a literature review should not look like)
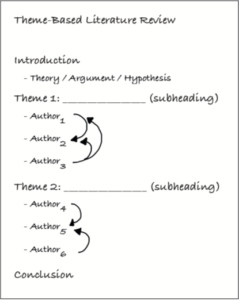
(This is what a literature review should look like!)
Based on the research I conducted, I created a four-step guide for UCWbL tutors to use when they are faced with a literature review appointment.
Step One: Does the Writer Understand the Assignment?
- Does the writer understand what a literature review entails? Discuss what context their review is functioning in.
Step Two: Check Source Comprehension/Personal Research
- Has the writer read all of the sources? Do they understand what each author is saying? Do they know what their research is trying to accomplish?
Step Three: Theme Identification
- What are the common themes among the sources? A quick explanation of the pros of an idea-driven review instead of an author-driven review.
Step Four: Start Outlining
- The graphic from the previous slide is really helpful for writers that are just starting out with a literature review and are unsure of exactly what to do.
While there is obviously no cookie cutter way to handle an appointment, I hope that this post helped to give you all a better idea of what a literature review is, and how to approach an appointment about one.
Thanks for reading and happy tutoring!
Sources
Burton, Jill. “Book Review: Literature Reviewing.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes, vol. 10, no. 1, 2011, pp. 61–64., doi:10.1016/j.jeap.2010.07.003.
Cisco, Jonathan. “Teaching the Literature Review: A Practical Approach for College Instructors.” Teaching & Learning Inquiry: The ISSOTL Journal, vol. 2, no. 2, 2014, pp. 41–57. JSTOR, JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/10.2979/teachlearninqu.2.2.41.
“Literature Reviews.” Writingcenter.unc.edu, writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/literature-reviews/.
“What Is a Literature Review?” The Royal Literary Fund, www.rlf.org.uk/resources/what-is-a-literature-review/.
Discover more from UCWbLing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
